兄弟们,上强度啦,你们觉得微服务搭建过程什么最重要?说实话,我也不清楚,但是我知道,规范一定是最重要的那部分之一
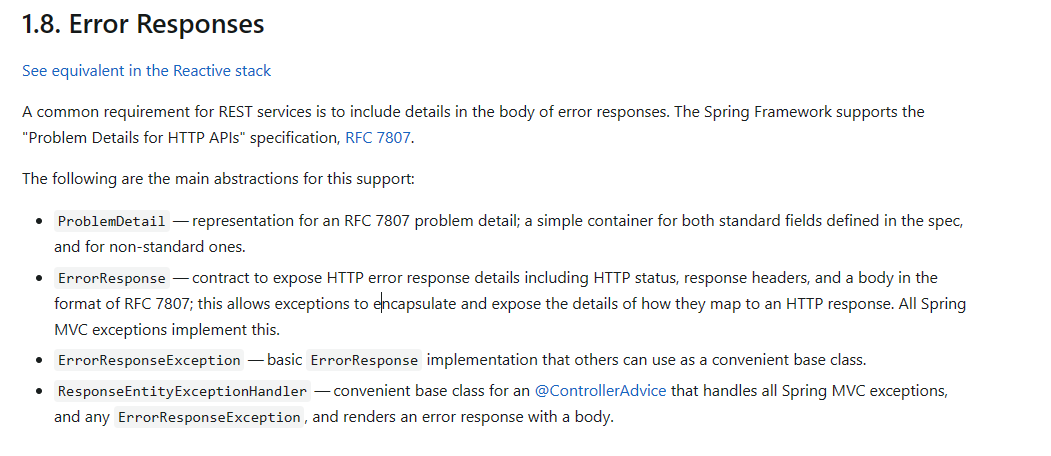
RFC 7807 定义
微服务规范最重要的就是服务间的调用,目前来说绝大多数都是restful接口,请求成功直接会返回业务数据,失败的话,一般都是抛出运行时异常,并统一捕获转化为对应的http状态码以及描述错误Json内容,这部分一般都是自定义的,但最近我看到了Spring最新官方文档其中Error Responses部分
![]()
是的,错误部分也有了一个规范,它包含五个部分
- type: 问题描述文档地址,如果不存在,则”about:blank”
- title: 简短的描述问题
- status: http 状态码,比如400、401、500等
- detail: 详细说明发生问题的原因
- instance: 问题发生的URL地址
这个和我原本自定义的错误内容差不多,所以,在这次搭建过程中,就使用了规范的定义,接下来就介绍我的开源项目J Cloud Platform中micro-common模块
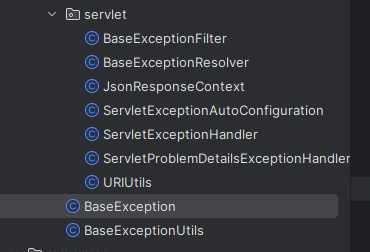
创建 micro-common 模块
像之前基础业务模块一样,创建一个micro-common模块,然后,修改pom.xml文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.jtj.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>parent</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>micro-common</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<name>micro-common</name>
<description>micro-common</description>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webflux</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
|
创建一个BaseException继承ErrorResponseException,不用原本的ErrorResponseException是因为难用,明明ProblemDetail已经包含HttpStatusCode,但在创建ErrorResponseException的时候,都得传(反正自定义一个不会错的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class BaseException extends ErrorResponseException {
public BaseException(HttpStatusCode status) {
super(status);
}
public BaseException(ProblemDetail body) {
this(body, null);
}
public BaseException(ProblemDetail body, @Nullable Throwable cause) {
super(HttpStatusCode.valueOf(body.getStatus()), body, cause);
}
}
|
创建一个BaseExceptionUtils工具类,用于更方便的创建异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| public class BaseExceptionUtils {
public static BaseException badRequest(String msg) {
return from(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, msg, null);
}
public static BaseException unauthorized(String msg) {
return from(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED, msg, null);
}
public static BaseException forbidden(String msg) {
return from(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN, msg, null);
}
public static BaseException notFound(String msg) {
return from(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, msg, null);
}
public static BaseException internalServerError(String msg) {
return from(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, msg, null);
}
public static BaseException internalServerError(String msg, @Nullable Throwable cause) {
return from(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, msg, cause);
}
public static BaseException from(HttpStatus status, String msg, @Nullable Throwable cause) {
ProblemDetail problem = ProblemDetail.forStatus(status);
problem.setTitle(status.getReasonPhrase());
problem.setDetail(msg);
return new BaseException(problem, cause);
}
}
|
Reactive 应用自动配置
接下来为Web应用配置统一的处理异常,先配置Reactive应用
创建一个BaseExceptionHandler继承WebExceptionHandler,Reactive应用的异常会在WebExceptionHandler依次处理,默认的WebExceptionHandler是0,所以需要修改位更小的数字,使它在默认前拦截异常,我们只拦截RuntimeException的异常,是因为其他异常如果发现应该在业务代码中拦截修复
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| @Slf4j
@Order(ORDER)
public class BaseExceptionHandler implements WebExceptionHandler {
public final static int ORDER = -100;
@Resource
private NoViewResponseContext context;
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Throwable throwable) {
if (throwable instanceof BaseException bex) {
URIUtils.update(bex, exchange);
return ServerResponse.from(bex)
.flatMap(serverResponse -> serverResponse.writeTo(exchange, context));
}
if (throwable instanceof RuntimeException ex) {
BaseException wrapper = BaseExceptionUtils.internalServerError(ex.getMessage(), ex);
URIUtils.update(wrapper, exchange);
return ServerResponse.from(wrapper)
.flatMap(serverResponse -> serverResponse.writeTo(exchange, context));
}
return Mono.error(throwable);
}
}
|
ServerResponse可以直接由BaseException创建,但它将输入写入ServerWebExchange需要一个Context,级一些编译解密器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class NoViewResponseContext implements ServerResponse.Context {
@Resource
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
@Override
public List<HttpMessageWriter<?>> messageWriters() {
return serverCodecConfigurer.getWriters();
}
@Override
public List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers() {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
|
BaseExceptionHandler还有个URIUtils,用于添加instance
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class URIUtils {
public static void update(BaseException ex, ServerWebExchange exchange) {
URI uri = ex.getBody().getInstance();
if (uri == null) {
String path = exchange.getRequest().getPath().value();;
ex.setInstance(URI.create(path));
}
}
}
|
最后,将我们的这些Bean注入到Spring中去
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @AutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE)
public class ReactiveExceptionAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public BaseExceptionHandler baseExceptionHandler() {
return new BaseExceptionHandler();
}
@Bean
public NoViewResponseContext noViewResponseContext() {
return new NoViewResponseContext();
}
}
|
@AutoConfiguration其实与@Configuration功能是一样的,一般用于有条件加载的情况下,例如上面,@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE) 表示在 REACTIVE 的 web 应用环境下加载
其实如果你去看了眼Spring官网文档的话,你会看到还可以用ResponseEntityExceptionHandler进行配置,但是,它只能转换注解的模式也就是@RequestMapping下,笑死,我要统一异常处理,那么必然是要连函数式模式也支持的
最后,在META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports中添加自动配置类ReactiveExceptionAutoConfiguration
Servlet 应用自动配置
Reactive 好了之后创建 Servlet 的配置,你或许会觉得他们应该差不多吧。刚开始我也是这么想的。但是servlet有三个地方处理异常HandlerExceptionResolver Filter ResponseEntityExceptionHandler,他们每个有自己的作用范围
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler: 只处理注解模式下的异常Filter: 处理注解模式下的异常和Filter中的异常HandlerExceptionResolver: 处理函数式模式下的异常
我当时调试的时候,真的想@#&%x~
![]() 其他方便差不多到我的开源项目 J Cloud Platform上看吧,不想贴源码了
其他方便差不多到我的开源项目 J Cloud Platform上看吧,不想贴源码了
如何使用
父模块中添加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jtj.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>micro-common</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
|
在业务模块中添加依赖就好了
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.jtj.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>micro-common</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
 其他方便差不多到我的开源项目 J Cloud Platform上看吧,不想贴源码了
其他方便差不多到我的开源项目 J Cloud Platform上看吧,不想贴源码了